Conceptual Architecture
Enterprise Architecture
This document outlines the comprehensive enterprise architecture for the NFM Payment Gateway using Google Cloud Platform's managed services.
The NFM Payment Gateway is designed as a distributed system composed of decoupled microservices, each with specific responsibilities. The system communicates via well-defined APIs (synchronously through API Gateway) or asynchronously via event bus (Cloud Pub/Sub).
System Architecture
Microservices Infrastructure (GCP Serverless)
- User & Agent Management Service (Cloud Run): Manages House, Agent users, profiles, permissions, API key generation. (Prisma + Cloud SQL)
- Device Management Service (Cloud Run/Functions): Registers agent devices, manages credentials, tracks status (Firestore for real-time updates). (Prisma + Cloud SQL, Firestore)
- Transaction Ingestion API (Cloud Function/Run): Secure endpoint for devices/clients to submit recharge data and payout requests. Publishes raw data to Pub/Sub.
- Recharge Processing Service (Cloud Run): Consumes recharge events from Pub/Sub, validates, processes, calculates fees, updates database, triggers notifications. (Prisma + Cloud SQL)
- Payout Orchestration Service (Cloud Run): Consumes payout request events, validates, triggers device communication, updates status. (Prisma + Cloud SQL)
- Device Communication Service (Cloud Run/Functions): Securely communicates instructions to agent devices for payouts and receives status updates.
- Notification Service (Cloud Functions): Manages webhook delivery to agent URLs for validated transactions. Handles retries via Pub/Sub. (Cloud SQL for webhook configs)
- Fee Calculation Service (Cloud Function): Centralized logic for calculating service fees. (Reads rules from Cloud SQL or config)
- Reporting Service (Cloud Run): Aggregates data, provides APIs for reports. (Prisma + Cloud SQL, potential denormalized views or BigQuery for complex analytics if needed later).
- Admin Service (Cloud Run): Backend for the House Admin Panel. (Interacts with other services)
Core Architectural Principles Addressed
- Auto-scaling: Cloud Run and Cloud Functions scale automatically based on demand (down to zero). Cloud SQL can be configured for auto-scaling storage and read replicas.
- Microservices: Clearly defined services with independent concerns.
- Caching: Cloud Memorystore for Redis for frequent data. API Gateway and Cloud CDN (via Load Balancer) for response caching.
- Cost-Effective: Pay-per-use model of serverless components. Low concurrency (20-100 users) fits this model perfectly. Scaling to zero when not in use significantly reduces costs.
- Less or zero cloud management and maintenance: Managed services (Cloud Run, Cloud Functions, Cloud SQL, Pub/Sub, Firestore, API Gateway) minimize infrastructure overhead.
- Monitoring (Core Features): Google Cloud Monitoring provides default metrics for all services (request count, latency, errors). Custom metrics can be added for business KPIs.
- Good Security:
- GCP IAM for access control.
- Google Cloud Secret Manager for API keys, database credentials.
- Cloud API Gateway for managing and securing APIs (auth, rate limiting).
- VPC Service Controls and Firewall rules.
- Secure communication (HTTPS) enforced.
- Firebase Authentication for UI users.
- Input validation and sanitization in all services.
C4 Architecture
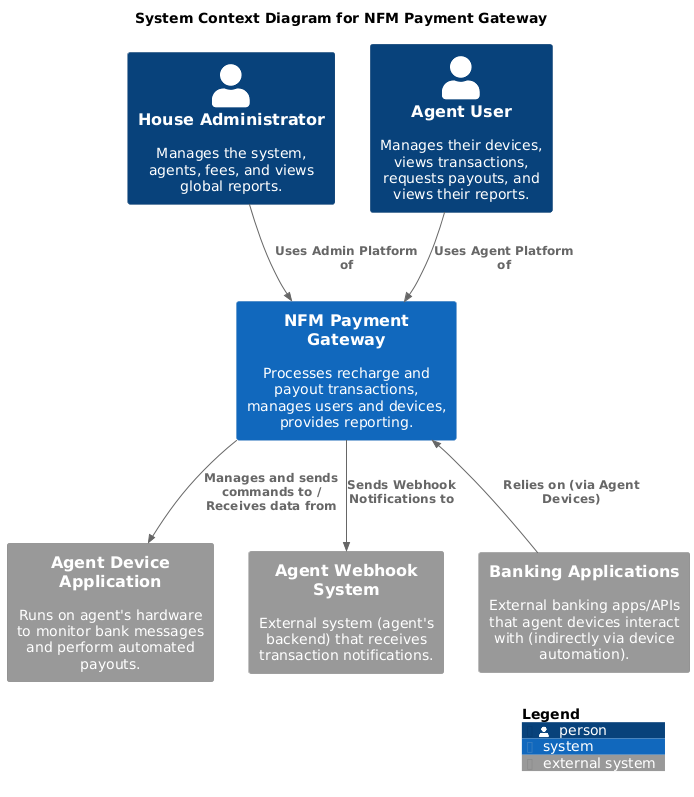
Level 1: System Context
The System Context diagram shows the NFM Payment Gateway in its environment, including key users and external systems.
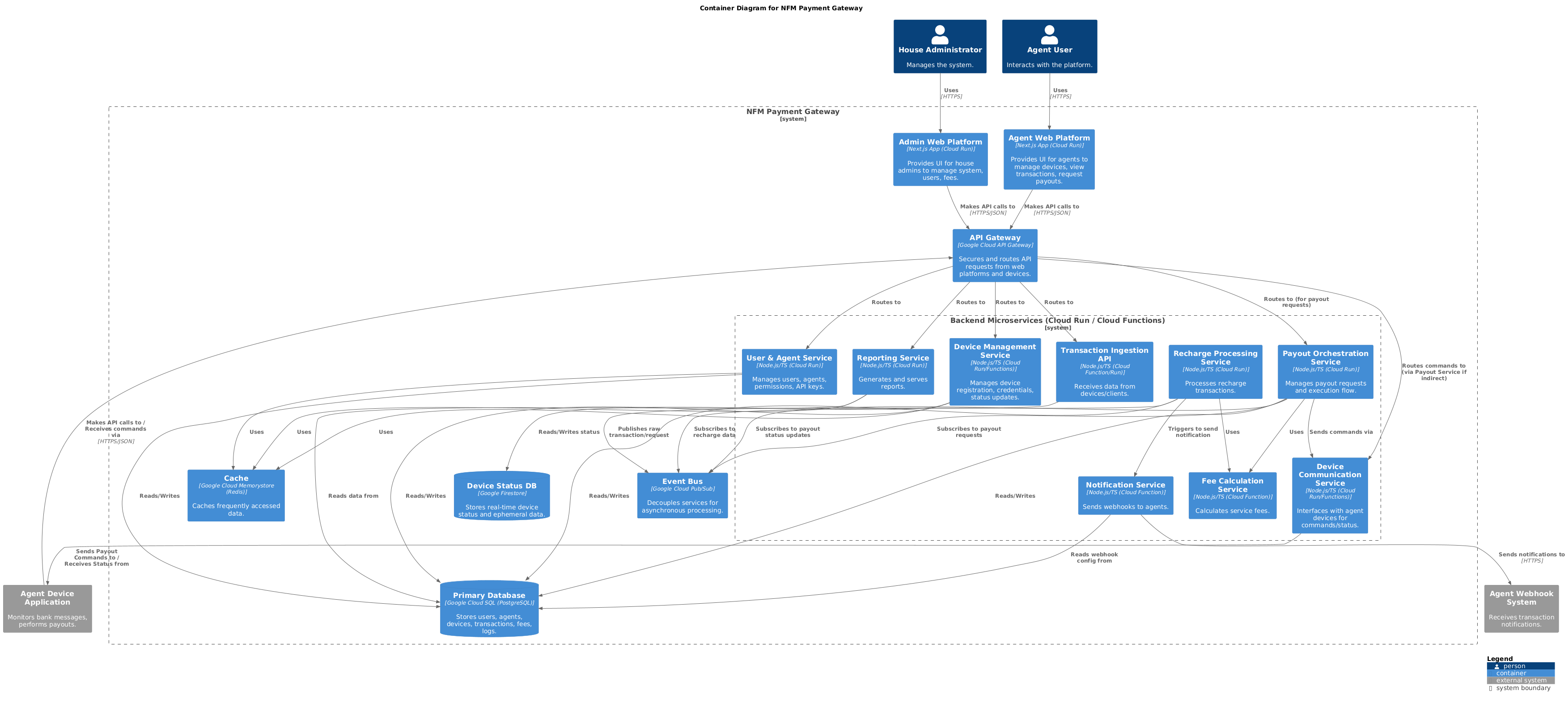
Level 2: Container Diagram
The Container diagram shows the high-level technical building blocks of the system.
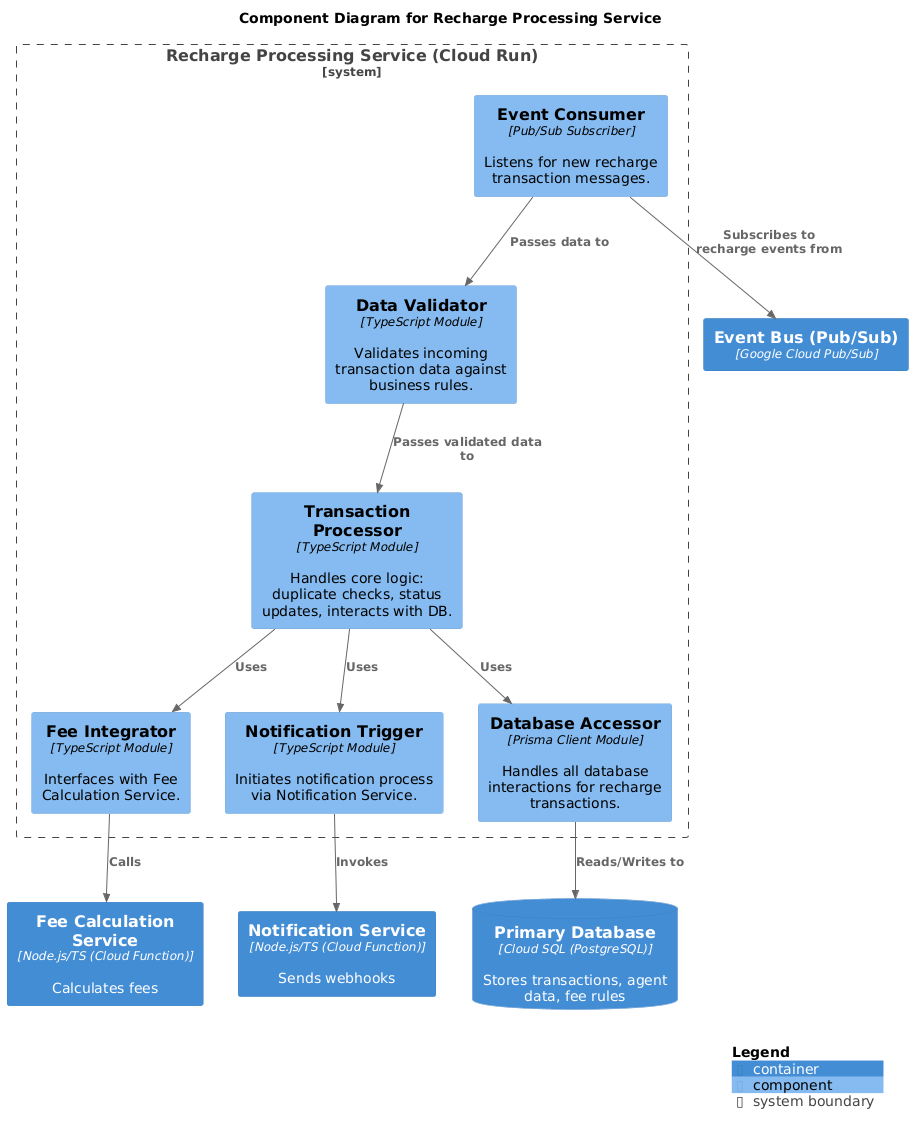
Level 3: Component Diagram
Example component breakdown for the Recharge Processing Service:
Workflow Modeling
Coming Soon
Interactive Architecture with workflow diagrams modeling. The process start when the implementation plan is ready.
Microservices Architecture
Core Services
User & Agent Management Service
- Manages user accounts and profiles
- Handles API key generation
- Controls permissions and access
Device Management Service
- Device registration and tracking
- Status monitoring
- Credential management
Transaction Processing Services
- Recharge data ingestion
- Payout processing
- Fee calculation
Notification Service
- Webhook delivery
- Retry management
- Status tracking
Database Design
Primary Database (PostgreSQL)
model User {
id String @id @default(cuid())
email String @unique
hashedPassword String?
role UserRole
name String?
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt
apiKey ApiKey?
agentProfile AgentProfile?
}
model Transaction {
id String @id @default(cuid())
type TransactionType
status TransactionStatus
amount Decimal
currency String
agentId String
agent AgentProfile @relation(fields: [agentId], references: [id])
serviceFee Decimal?
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt
}
Secondary Database (Firestore)
Used for:
- Real-time device status
- Live transaction updates
- Caching frequently accessed data
Security Implementation
Authentication & Authorization
User Authentication
- Firebase Authentication for UI users
- JWT validation
- Session management
API Security
- API key validation
- Request signing
- Rate limiting
Data Security
Encryption
- Data at rest encryption
- TLS for data in transit
- Secure key management
Access Control
- IAM roles and permissions
- Service account management
- Principle of least privilege
Deployment Architecture
Infrastructure as Code
All infrastructure is managed using Terraform:
resource "google_cloud_run_service" "user_service" {
name = "user-service"
location = "us-central1"
template {
spec {
containers {
image = "gcr.io/project/user-service:latest"
resources {
limits = {
cpu = "1000m"
memory = "512Mi"
}
}
}
}
}
}
CI/CD Pipeline
Build Stage
- Code linting
- Unit tests
- Container building
Deploy Stage
- Terraform validation
- Infrastructure updates
- Service deployment
Implementation Timeline
Phase 1: Foundation (2-3 weeks)
- Infrastructure setup
- CI/CD pipeline
- Basic service structure
Phase 2: Core Services (3-4 weeks)
- User management
- Device registration
- Basic transaction handling
Phase 3: Advanced Features (4-6 weeks)
- Complete transaction processing
- Reporting system
- Admin controls
Phase 4: Testing & Launch (3-4 weeks)
- Security hardening
- Performance testing
- Documentation
- Production deployment
Total Timeline: 19-26 weeks