Conceptual Architecture
Architecture guide
The NFM Payment Gateway is a modern, microservices-based payment system built using a serverless-first approach. This overview introduces the key concepts and architecture of the system.
Core Principles
Our system is built on these fundamental principles:
- Serverless First: Utilizing GCP Cloud Functions/Cloud Run for event-driven, stateless services
- API-Driven: All communication via well-defined APIs
- Event-Driven: Using GCP Pub/Sub for asynchronous communication
- Managed Services: Leveraging managed services to reduce operational overhead
- Security by Design: Implementing multi-layer security
Architecture Overview
The system is composed of decoupled microservices, each with specific responsibilities:
Frontend Applications
- Management Platform: Next.js-based interface for House administration and Agent operations
- Deployment: Google Cloud Run with SSR capabilities
Core Services
- User & Agent Management: Handles user accounts, profiles, and permissions
- Device Management: Manages device registration and status tracking
- Transaction Processing: Handles recharge and payout operations
- Reporting: Provides comprehensive transaction analytics
Key Technologies
Tech Stack Highlights
- Frontend: Next.js with TypeScript & Tailwind CSS
- Backend: Node.js with TypeScript
- Database: PostgreSQL (Cloud SQL) & Firestore
- Message Bus: Google Cloud Pub/Sub
- Authentication: Firebase Authentication
System Context
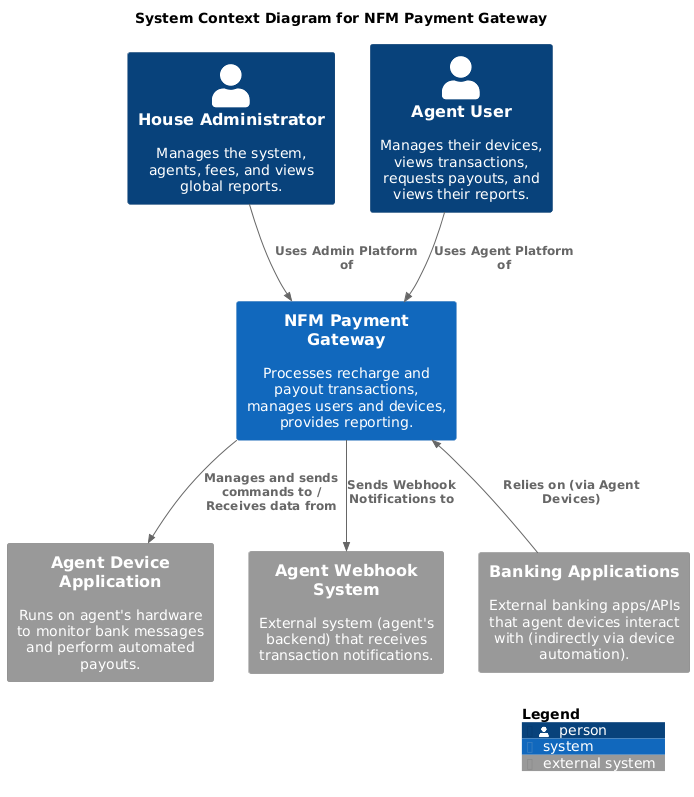
The system interacts with several external actors:
- House Administrators
- Agents
- Payment Devices
- External Banking Systems
Data Flow Examples
Recharge Workflow
- Agent device fecthing recharge transaction data
- Transaction is validated and processed
- Fees are calculated
- Notifications are sent to relevant parties
- Transaction is recorded for reporting
Payout Workflow
- Agent initiates payout request
- Request is validated against balance/limits
- Appropriate device is selected for automation
- Payout is executed and status tracked
- Transaction is recorded and notifications sent